“[Viral meningitis] is fairly easy to spread but it can be prevented fairly easily too,” school nurse Paula Hatcher said “[it’s as easy as] careful hand washing, and keeping your own drinks to yourself”.
What Is Meningitis?
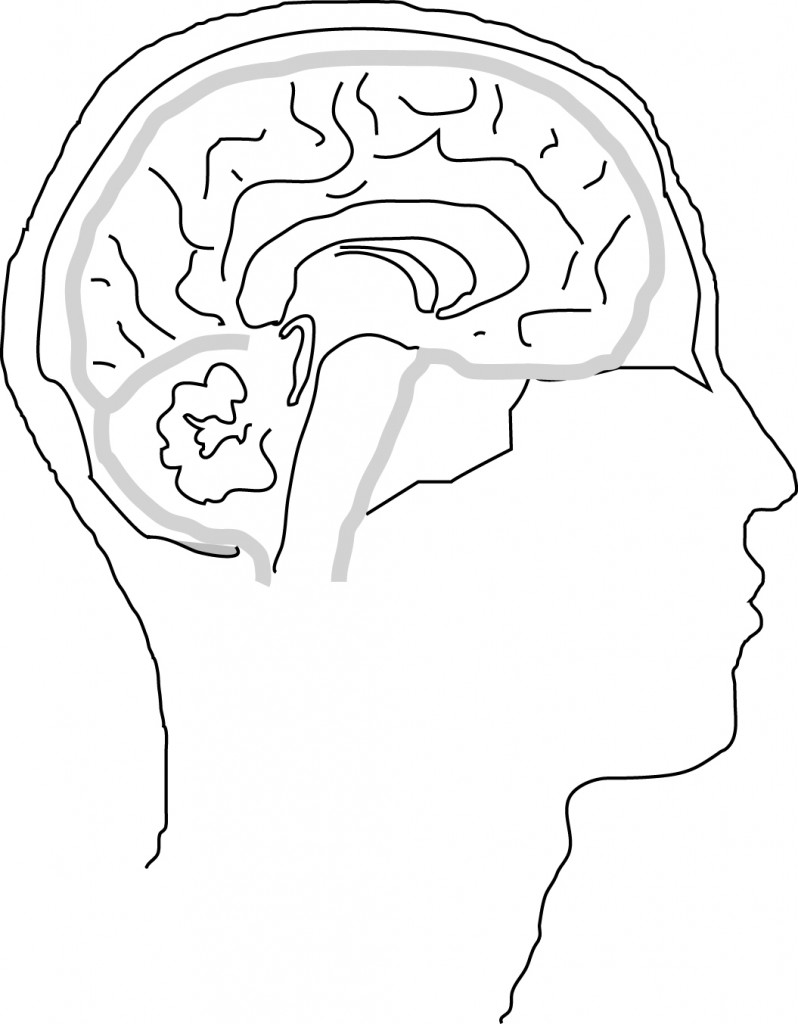
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes (meninges) that cover the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis is usually caused by a viral or bacterial infection says the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The two main types of meningitis are viral and bacterial. Other types include fungal, parasitic, and some with non-infectious causes, but these are very rare. Meningitis is spread like a cold, it can be spread by sneezing, shaking hands, and other things of the sort.
Viral vs Bacterial
Knowing whether meningitis is caused by a virus or bacterium is important because the severity of illness and the treatment differ depending on the cause. Viral meningitis is generally less severe and clears up without specific treatment. Symptoms last about seven to ten days and the infected will recover completely. CDC advises the best treatment for the viral strand is bed rest, medicine for fevers and headaches, and plenty of fluids.
Bacterial meningitis is extremely serious. Medical attention should be sought immediately if symptoms appear. Bacterial meningitis has a much higher fatality rate than its viral cousin and has been known to cause brain damage, hearing loss, and learning disabilities. A vaccine exists for bacterial meningitis and is recommended for all high school students and required to get into some colleges.
Symptoms of Meningitis
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Sensitivity to bright light
- Sleepiness or trouble waking up
- Nausea, vomiting
- Lack of appetite